The task of turning alternating current into direct current is called rectification, and the electronic circuit that does the job is called a rectifier. The most common way to convert alternating current into direct current is to use one or more diodes, those handy electronic components that allow current to pass in one direction but not the other.
Although a rectifier converts alternating current to direct current, the resulting direct current isn’t a steady voltage. It would be more accurate to refer to it as “pulsating DC.” Although the pulsating DC current always moves in the same direction, the voltage level has a distinct ripple to it, rising and falling a bit in sync with the waveform of the AC voltage that’s fed into the rectifier.
For many DC circuits, a significant amount of ripple in the power supply can cause the circuit to malfunction. Therefore, additional filtering is required to “flatten” the pulsating DC that comes from a rectifier to eliminate the ripple.
There are three distinct types of rectifier circuits you can build: half-wave, full-wave, and bridge.
The rectifier allows the alternating current to pass through one direction, but does not allow it to oscillate back the other direction. Here’s what happens with a single diode, basic rectifier circuit:
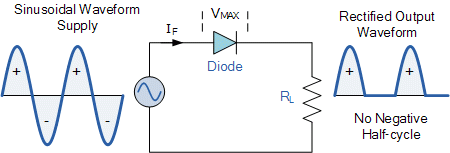
As you can see, the output has no negative current values. In order to produce a straight line direct current, like what you get from a battery, you would have to use full-bridge rectifiers which consist of a complex schematic.

Rectifiers are widely used in the metallurgical industry, mainly in…
Basic principle of rectifier for electrolytic hydrogen production: Electrolysis of…
Liyuan Haina Rectifier, the professional manufacturer in IGBT and SCR rectifier, committed to providing you with quality solutions and products.
Get more details? We’ll response as soon as possible (within 12 hours).
Liyuan Haina Rectifier, the professional manufacturer in IGBT and SCR rectifier, committed to providing you with quality solutions and products.
Get more details? We’ll response as soon as possible (within 12 hours).